Introduction
Kubernetes is an open source container management system, and in this post, we will deploy the Apache web server on Kubernetes.
Details about the Kubernetes components
- API Server – Intract with kubectl command utility, Primary component, Authorization work.
- Controller Manager – Replica controller, Node Controller maintainer the define pods and nodes.
- Scheduler – Matain proper balacing of hardware utilization and assign new pods to sutable workder node as per ranking.
- ECTD – Database its store the data using key and value form format.
- Kubelet – Pod moniotr, Pod creation and deletation.
- Kube-proxy – Pods communication between 2 nodes, Network related rules manages by kube-proxy.
Step 1: Write a Deployment YAML
We need to write a deployment YAML file with named like apache-deployment.yaml, You can use the given code in order to deploy the Apache docker container in K8s.
nano apache-deployment.yamland paste the following code.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: apache
labels:
app: apache
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: apache
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: apache
spec:
containers:
- name: apache
image: ubuntu/apache2
ports:
- containerPort: 80Take a look at the above YaML configuration:
apiVersion: Define the Kubernetes API in order to create objects.
kind: specify the type of object you intend to create.
metadata: define the object name ( including a name string, uniquely identifying the object, the UID, and an optional namespace ).
spec: Define the state of objects.
selector: specify the mapping between deployment and managed pods.
We need to save and exit from text editor, Our deployment YAMl is ready Lets deplot the apache pod on K8s cluster.
Step 2: Create a Deployment
We need to execute the following command to deploy the apache pods which is container apache image.
kubectl create -f apache-deployment.yamlYou will get sucess message for the apache deployment on your screen.
We will get a single pod of the Apache image and, according to the Dockerfile configuration, Apache will be up and running on port 80.
Step 3: Let’s Verify the Deployment
We need to execute the given command to see pods and ruuning or not.
To Validate the pod.
kubectl get podsTo check deployment.
kubectl get deploymentYou should get output like this.
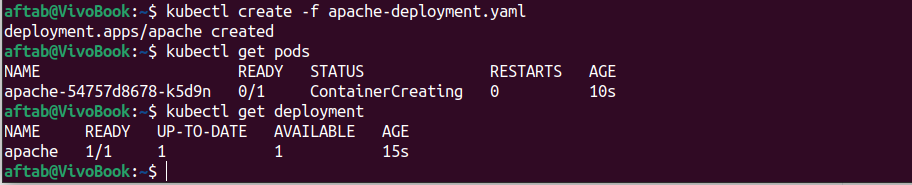
Step 4: Create a Service
We need to create a apache-service.yaml file in order access apache web server, Create a apache-service.yaml file with follwing code.
To create a service.yaml file
nano apache-service.yamlPaste the following code.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: apache-service
spec:
selector:
app: apache
type: NodePort
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80The Kubernetes service section: K8s services allow network access to the set of pods.
port: Define the application’s port inside the Docker container.
nodePort: The port number to use to connect to the base machine.
protocol: define a network layer type like TCP/UDP, To communicate with the network.
selector: To know and identify the deployment-created objects.
Save and close the text editor. As per our service configuration, we define port 80 to access the Apache web server, which is mapped with a label like app: apache, We are using NodePort to access the Apache web server on each node using port 80.
Step 5: Deploy Service
We need to execute the given command to deploy the apache-service on K8s cluster.
kubectl create -f apache-service.yamlWe should get a success message on the screen, To check the service status for Apache, execute the given command.
To get service status.
kubectl get svc Here we can see that NodePort assigned the random port to access the Apache web server on each node.
Note: If you are using minikube So you need to use the given command to expose the total url to access your kubernets application.
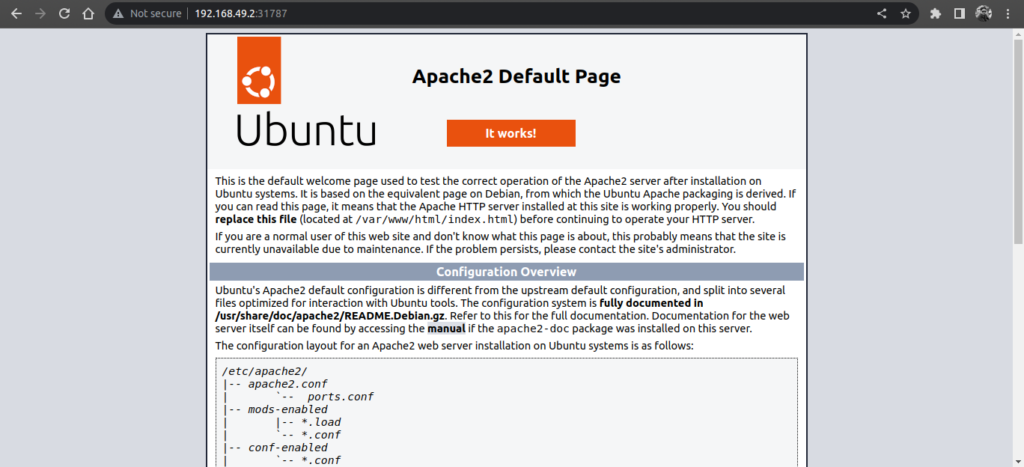
minikube service apache-service --urlYou should get output like this.

Apache test page demo.
Step 6: Clean Up
Our Apache web server deployment is complete, and we can now delete all of the resources that we deployed a few minutes ago with the following command.
To get apache service name.
kubectl get svcTo destory the apache service.
kubectl delete svc apache-service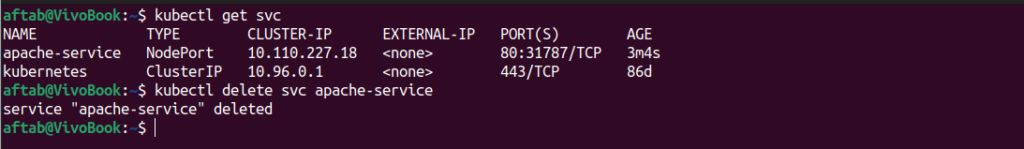
To get apache deployment.
kubectl get deploymentTo destory apache deployment.
kubectl delete deployment apache
To validate the previous action.
kubectl get allYou should get an output like this from the previous kubectl command execution.

Conclusion
We have successfully deploy apache web server on kubernetes cluster in a simple way, If you still have questions, please post them in the comments section below.

nice work.